胸腺肽、胸腺五肽、胸腺法新之间的区别,应如何选择?
时间:2022-03-02 12:09:07 热度:37.1℃ 作者:网络
作为人体的天然屏障的自身免疫力,对内可以维持人体稳态,对外可防御侵扰。但对于自身免疫力低下的癌症患者来说,胸腺肽、胸腺五肽、胸腺法新则成了提高免疫力的有力武器。
他们到底是什么呢?我们得先来了解一下胸腺。
胸腺是免疫系统的一个特殊的原发性淋巴器官。在胸腺内,胸腺细胞淋巴细胞或T细胞成熟。T细胞对适应性免疫系统至关重要,身体特别适应外来入侵者。胸腺位于胸部前部、纵隔前部、胸骨后方和心脏前方。而胸腺肽类即为胸腺激素,能够调节免疫系统,对机体的免疫反应具有激活作用,可以增加集体的免疫应答,最终达到增加机体抗病和抗感染能力,又称免疫刺激剂。
 胸腺肽(thymosin):是胸腺组织分泌的具有生理活性的一组多肽。临床上常用的胸腺肽是从小牛胸腺发现并提纯的有非特异性免疫效应的小分子多肽。
胸腺五肽(thymopentin):由缬氨酸、精氨酸、赖氨酸、酪氨酸、天门冬氨酸五种氨基酸组成,是胸腺生成素Ⅱ的有效部分。我国目前胸腺五肽制剂是以氨基酸为原料,作为人工合成化合物。胸腺五肽有结构明确,纯度较高等特点。
胸腺法新(thymalfasin):又叫胸腺肽α1,是由胸腺素组分 5(TF-5) 中分离纯化分离出的一种小分子生物活性多肽,具有较高的免疫增强活性。
那么他们之间到底该如何选择呢?我们就按照以下几个方向进行药物之间的对比:
胸腺肽(thymosin):是胸腺组织分泌的具有生理活性的一组多肽。临床上常用的胸腺肽是从小牛胸腺发现并提纯的有非特异性免疫效应的小分子多肽。
胸腺五肽(thymopentin):由缬氨酸、精氨酸、赖氨酸、酪氨酸、天门冬氨酸五种氨基酸组成,是胸腺生成素Ⅱ的有效部分。我国目前胸腺五肽制剂是以氨基酸为原料,作为人工合成化合物。胸腺五肽有结构明确,纯度较高等特点。
胸腺法新(thymalfasin):又叫胸腺肽α1,是由胸腺素组分 5(TF-5) 中分离纯化分离出的一种小分子生物活性多肽,具有较高的免疫增强活性。
那么他们之间到底该如何选择呢?我们就按照以下几个方向进行药物之间的对比:
安全性、有效性
药理作用
用法用量
价格,注意事项等等
随着★增加,药物越来越好!(先做表格总结)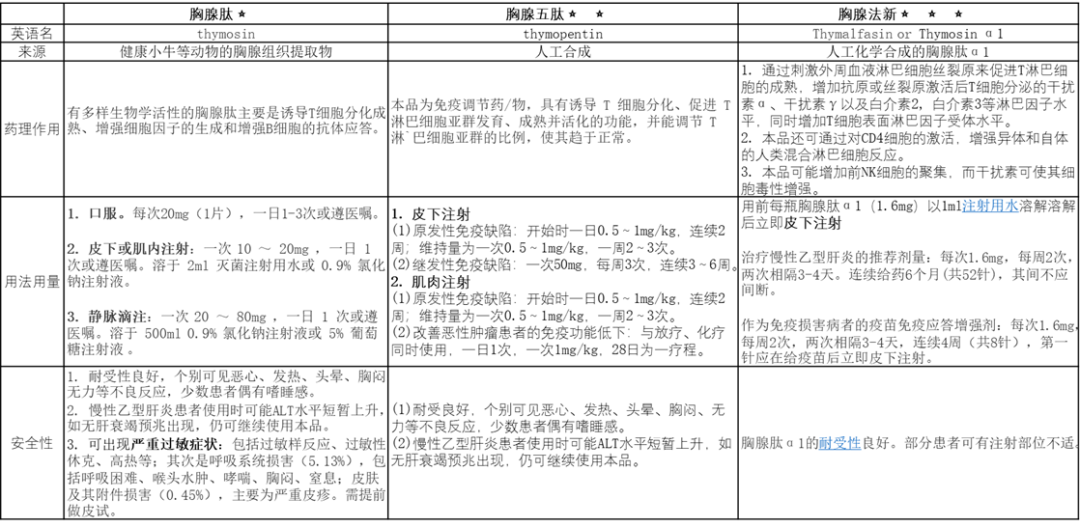
 总结:
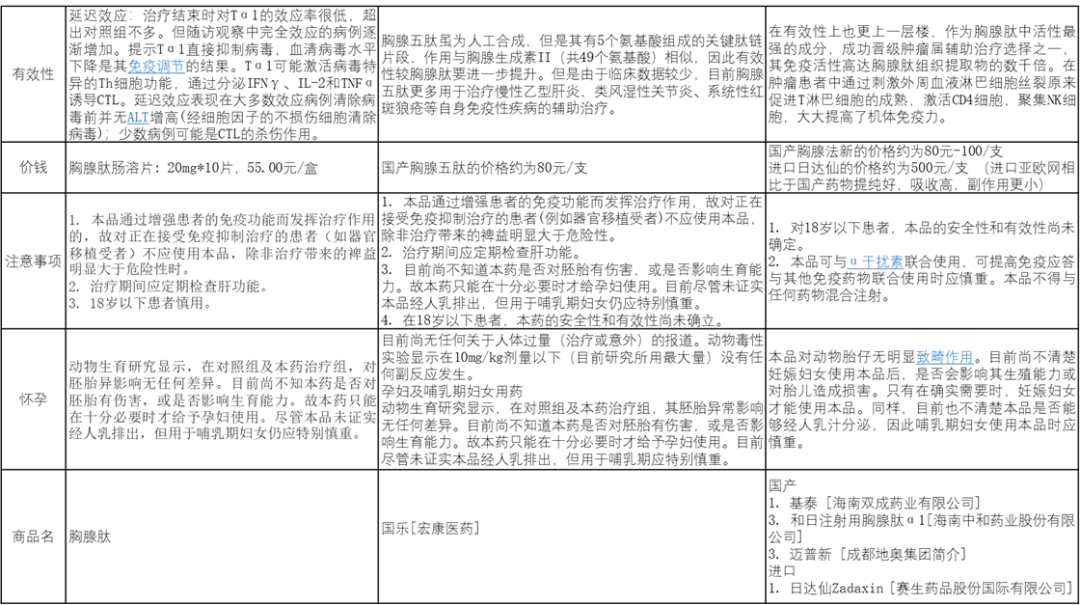
1、安全性
胸腺肽:是从动物胸腺组织中提取的天然物质,因此含动物致敏大分子蛋白,有效成分尚未确定。因此存在安全相对较差,在特殊人群中会出现严重的过敏反应,使用前患者需进行试敏。
胸腺五肽:由于胸腺五肽并非人体天然存在物质,因此作用在人身上时,并未展现良好的贴合性,因此,安全性介于胸腺肽及胸腺法新之间。
胸腺法新:亦是人工合成,但是有别于胸腺五肽,其功能结构进一步的贴合人体天然成分胸腺肽α1,因此发生过敏反应概率微乎其微,患者无需做皮试即可安全使用。
2、有效性
胸腺肽:目前由于安全性较差的缘故,临床应用较少,尤其对于孕妇或哺乳期女性要格外慎用。目前多用于治疗慢性乙型肝炎、抗肿瘤,以及喘息性支气管炎、系统性红斑狼疮等疾病。
胸腺五肽:胸腺五肽虽为人工合成,但是其有5个氨基酸组成的关键肽链片段,作用与胸腺生成素II(共49个氨基酸)相似,因此有效性较胸腺肽要进一步提升。但是由于临床数据较少,目前胸腺五肽更多用于治疗慢性乙型肝炎,类风湿性关节炎、系统性红斑狼疮等自身免疫性疾病的辅助治疗。
胸腺法新:在有效性上也更上一层楼,作为胸腺肽中活性最强的成分,成功晋级肿瘤届,成为辅助治疗选择之一,其免疫活性高达胸腺肽组织提取物的数千倍。在肿瘤患者中通过刺激外周血液淋巴细胞丝裂原来促进T淋巴细胞的成熟,激活CD4细胞,聚集NK细胞,大大提高了机体免疫力。
因此,从胸腺肽到胸腺五肽,再到胸腺法新,无论是安全性还是有效性都有质的飞跃。
日达仙(zadaxin):进口胸腺法新日达仙可应用于很多不同疾病状态中,例如乙肝,丙肝和癌症患者辅助治疗提高免疫疗法。以下对各个文章进行分析汇总,着重观察日达仙的responserate, 有效性相比于安慰剂或其他组别药物,其在各个疾病中都展现出独有的优势。
治疗慢性乙肝有效性(HBV):
总结:
1、安全性
胸腺肽:是从动物胸腺组织中提取的天然物质,因此含动物致敏大分子蛋白,有效成分尚未确定。因此存在安全相对较差,在特殊人群中会出现严重的过敏反应,使用前患者需进行试敏。
胸腺五肽:由于胸腺五肽并非人体天然存在物质,因此作用在人身上时,并未展现良好的贴合性,因此,安全性介于胸腺肽及胸腺法新之间。
胸腺法新:亦是人工合成,但是有别于胸腺五肽,其功能结构进一步的贴合人体天然成分胸腺肽α1,因此发生过敏反应概率微乎其微,患者无需做皮试即可安全使用。
2、有效性
胸腺肽:目前由于安全性较差的缘故,临床应用较少,尤其对于孕妇或哺乳期女性要格外慎用。目前多用于治疗慢性乙型肝炎、抗肿瘤,以及喘息性支气管炎、系统性红斑狼疮等疾病。
胸腺五肽:胸腺五肽虽为人工合成,但是其有5个氨基酸组成的关键肽链片段,作用与胸腺生成素II(共49个氨基酸)相似,因此有效性较胸腺肽要进一步提升。但是由于临床数据较少,目前胸腺五肽更多用于治疗慢性乙型肝炎,类风湿性关节炎、系统性红斑狼疮等自身免疫性疾病的辅助治疗。
胸腺法新:在有效性上也更上一层楼,作为胸腺肽中活性最强的成分,成功晋级肿瘤届,成为辅助治疗选择之一,其免疫活性高达胸腺肽组织提取物的数千倍。在肿瘤患者中通过刺激外周血液淋巴细胞丝裂原来促进T淋巴细胞的成熟,激活CD4细胞,聚集NK细胞,大大提高了机体免疫力。
因此,从胸腺肽到胸腺五肽,再到胸腺法新,无论是安全性还是有效性都有质的飞跃。
日达仙(zadaxin):进口胸腺法新日达仙可应用于很多不同疾病状态中,例如乙肝,丙肝和癌症患者辅助治疗提高免疫疗法。以下对各个文章进行分析汇总,着重观察日达仙的responserate, 有效性相比于安慰剂或其他组别药物,其在各个疾病中都展现出独有的优势。
治疗慢性乙肝有效性(HBV):
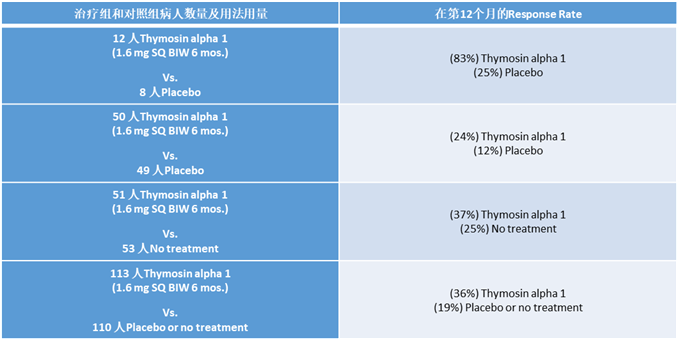
Placebo: 安慰剂
Thymosinalpha 1:胸腺法新
SQ:皮下注射
BIW:每周两次
Mos: 月
Responserate:定义为在12 个月随访时 HBV DNA 和 HBeAg 阴性的受试者的百分比
建议剂量:当用作单一疗法或与干扰素联合使用时,用于慢性乙型肝炎的ZADAXIN(胸腺嘧啶)的推荐剂量为1.6mg(900μg/m2),每周两次皮下给药,持续6至12个月。体重小于40 kg 的患者应接受40 μg/kg 的胸腺法新剂量。
治疗慢性丙肝有效性(HCV):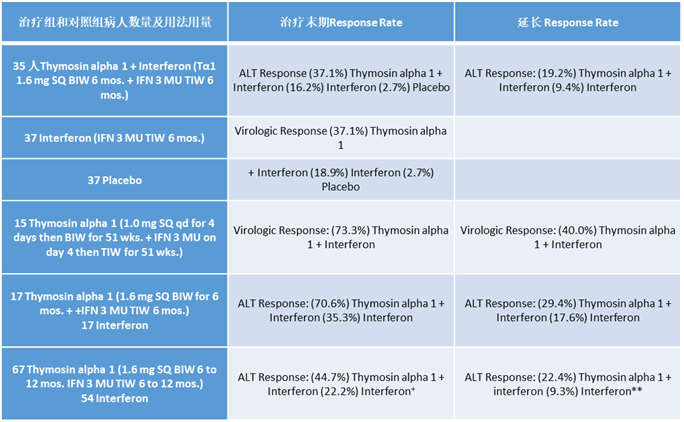
Placebo:安慰剂
Thymosinalpha 1:胸腺法新
SQ:皮下注射
Qd: 一日一次
BIW:每周两次
TIW:每周三次
Mos: 月
Responserate:定义为在12 个月随访时 HBV DNA 和 HBeAg 阴性的受试者的百分比
在癌症患者中: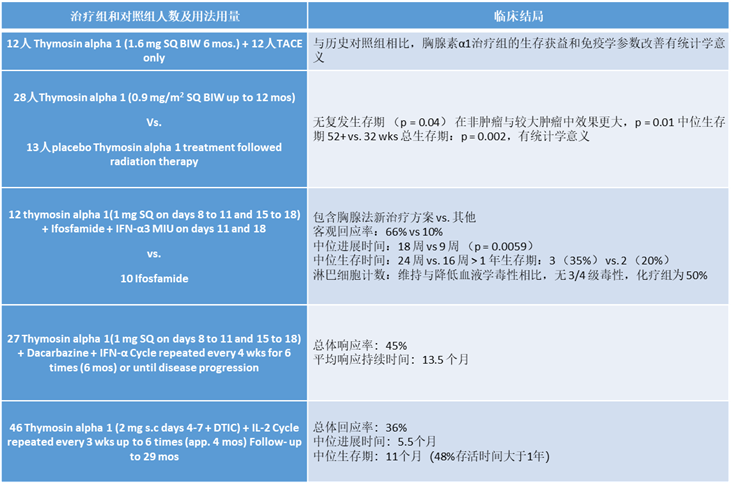
Placebo:安慰剂
Thymosinalpha 1:胸腺法新
Ifosfamide: 异环磷酰胺
Dacarbazine:达卡巴嗪
SQ:皮下注射
BIW:每周两次
TIW:每周三次
Mos: 月
Responserate:定义为在12 个月随访时 HBV DNA 和 HBeAg 阴性的受试者的百分比
TACE: 一种破坏肿瘤的技术,其中将管子引导到肿瘤的动脉血液供应中,并引入药物,肌肉碎片或合成球体以阻塞动脉。
radiationtherapy:放疗
diseaseprogression:疾病进展
Follow- up:随访
建议剂量:用于癌症的日达仙(ZADAXIN)的推荐剂量为1.6mg(900μg/ m2),皮下注射6个月,或在治疗期间在化疗周期之间给予。
参考文献:
1. Mutchnick, M.G., Cummings, G.D.,Hoofnagle, J.H., and D.A. Shafritz (1992) Thymosin: An innovativeapproach to the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, in Combinationtherapies BiologicalResponse Modifiers in the Treatment ofCancer and Infectious Diseases, A.L Goldstein and E. Garaci, Editors. PlenumPublishing Corp: New York. p. 149-156
2. Mutchnick, M.G., Lindsay, K.L.,Schiff, E.R., Cummings, G.D., and H.D. Appelman (1995) Thymosin alpha 1treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlleddouble blind
study Gastroenterology 108(4): p. A1127
3. Lee, S.-D., D.-S. Chen, and Y.-F. Liaw(1997) Multicenter Study of Thymosin Alpha 1 in the Treatment ofChronic Hepatitis B. Data on file.
4. Chien, R.-N., Liaw Y.-F., Chen, T.-C,Yeh, C.-T., and I.-S. Sheen (1998) Efficacy of Thymosin α1 in Patientswith Chronic Hepatitis B: A Randomized, Controlled TrialHepatology 27 (5) May 1998: p.1383-1387.
5. Niedzwiecki, D., Luo, D., Finn, D.S.,Whiting, G.W., Connelly, J.E., Kumashiro, M., Allen, I.E. and S.D. Ross(1997) The efficacy of thymosin alpha 1 in chronic hepatitis B: ameta-analysis, Data on file.
6. Sherman, K.E., Sjogren, M., Greager, R.L.Damiano, M.A., Freeman, S., Lewey, S. Davis, D., Root, S., Weber, F.L., IshakK.G., and Z.D. Goodman (1998) Combination Therapy with Thymosin alpha 1and Interferon for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Infection: ARandomized, Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind Trial, Hepatology 27 (4):p. 1128-1135
7. Rasi, G., DiVirgilio, D., Mutchnick,M.G., Colella, F, Sinibaldi-Vallebona, P., Pierimarchi, P. Balli, B., and E.Garaci (1996) Combination thymosin α1 and lymphoblastoid interferontreatment in chronic hepatitis C, Gut 39: p. 679-683.
8. Moscarella, S ., Buzzelli, G., MontiM., Giannini, C, Careccia, G. Marrochi, E.M., Romanelli, R.G. and A.L. Zignego(1997) Treatment with interferon-alpha and thymosin alpha 1 of naivepatients affected by chronic hepatitis C, in 4th International meetingon HepatitisC Virus and Related Viruses. Kyoto, Japan
9. Sherman, K.E., and S.N. Sherman(1997) Pooled analysis of interferon + thymosin alpha-1 efficacy forthe treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Second International Conferenceon Therapies for ViralHepatitis, Kona, Big Island Hawaii, December15-19: abstract #P50
10. Stefanini, G.F., et al., Alpha-1 thymosin and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in hepatocellularcarcinoma patients: a preliminary experienceHepatogastroenterology, 1988. 45 (19): p.209-215
11. Schulof, R.S., et al., A randomizedtrial to evaluate the immunorestorative properties of synthetic thymosin alpha1 in patients with lungcancer. Journal of Biological ResponseModifiers 1985 4: p. 147-158
12. Salvati, F, et al., Combinedtreatment with thymosin alpha 1 and low dose interferon-alpha after ifosfamidein non-smallcell lung cancer: a phase II controlledtrial. Anticancer Research 1996 16: p. 1001-1004
13. Rasi, G., Terzoli, E., lzzo, F., etal., Combined treatment with thymosin alpha 1 and low dose nterferon alphaafter dacarbazine in advanced melanoma. Melanoma Research 2000 10: p 189-192
14. Lopez, M, et al., Biochemotherapywith thymosin alpha 1, inteluken-2 and dacarbazine in patients with metastaticmelanoma: clinical and immunological effects. Annals of Oncology 1994 5: p. 741-746.


